請先看『使用說明』
DPC Module:DPC Console under Linux
From LEXWiKi
Contents |
The Sample code source you can download form
Binary file:
<Google Drive> DPC_Console_v1.0.0.4L_Bin_x64
<FTP> DPC_Console_v1.0.0.4L_Bin_x64
How to compile source code
- Compile source code with Code::Blocks.
- Download and install the Code::Block with command "apt-get install codeblocks".
- Open an exist project(DPC_Console.cbp) in Code::Blocks, click the compile button.
- Download and install the Code::Block with command "apt-get install codeblocks".
- Compile source code with "make"
- cd DPC_Console
- key in command "make".
- cd DPC_Console
Before you make it, you need to install : "make" "make-guile" "pkg-config" "gcc" "gtk2.0"
How to use the DPC console application
- Install resource before execute application. ".\install.sh"
- Execute the application. ".\DPC_Console".
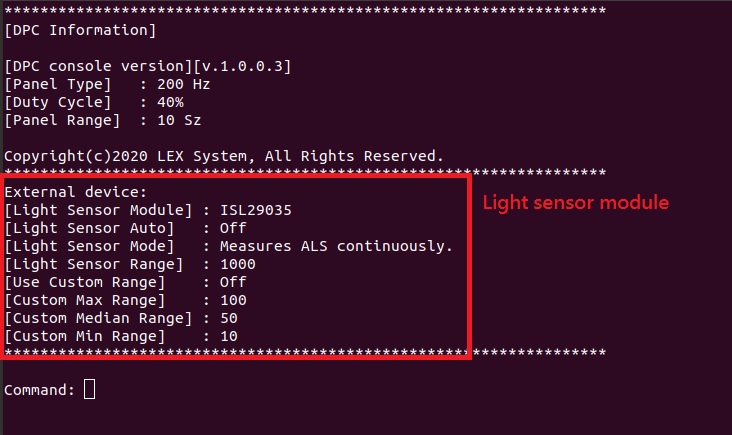
- Dump DPC information with command "-i".
- Print DPC help menu with command "-h".
- Set brightness from 10 to 100 with command "-d". Ex: Set brightness 50 with command "-d50".
- Select panel what you try to adjust with command "-t". Ex: Select 200 Hz with command "-t0".
(0 = 200 Hz, 1 = 275 Hz, 2 = 380 Hz, 3 = 20 Hz, 4 = 25 Hz)
- Select range what you add / subtract brightness with command "-r". Ex: Select 10 Sz with command "-r4".
(0 = 1 Sz, 1 = 2 Sz, 2 = 3 Sz, 3 = 5 Sz, 4 = 10 Sz)
- Step add / subtract brightness with keyboard : "Up arrow key" / "Down arrow key".
- Turn off screen backlight with command "-f". Duty cycle value will be modify to 0.
- Fixed hot key to turn on screen backlight with hot key "Ctrl + n". Duty cycle value will be modify to 50.
- Clear terminal screen with command "Clear".
- Quit DPC application with command "Exit".
If you have LEX light sensor module. How to use light sensor module
- Print light sensor help menu with command "-hl".
- Turn on/off light sensor to modify duty cycle value automaticaly. With command "-la". Ex: Turn off light sensor active with command "-la0".
(0 = Off, 1 = On)
Attention: If active light sensor module, GPIO module will be turned off.
- Select light sensor mode with command "-lm". Ex: Select ALS mode with command "-lm0".
(0 = Measures ALS continuously, 1 = Measures IR continuously)
- Select light sensor range with command "-lr". Ex: Select range 1000 with command "-lr0".
(0 = 1000, 1 = 4000, 2 = 16000, 3 = 64000)
- Turn on/off using custom bounding range with command "-lc". Ex: Turn on custom bounding range with command "-lc1".
(0 = Use, 1 = Not use)
- Set a custom value for light sensor maximum range with command "-lmax". Ex: Set 100 for maximum range with command "-lmax9".
(0 = 10, 1 = 20, 2 = 30, 3 = 40, 4 = 50, 5 = 60, 6 = 70, 7 = 80, 8 = 90, 9 = 100)
- Set a custom value for light sensor median range with command "-lmed". Ex: Set 50 for median range with command "-lmed4".
(0 = 10, 1 = 20, 2 = 30, 3 = 40, 4 = 50, 5 = 60, 6 = 70, 7 = 80, 8 = 90, 9 = 100)
- Set a custom value for light sensor minimum range with command "-lmin". Ex: Set 10 for minimum range with command "-lmin0".
(0 = 10, 1 = 20, 2 = 30, 3 = 40, 4 = 50, 5 = 60, 6 = 70, 7 = 80, 8 = 90, 9 = 100)
Sample code Introduction
Define SMBus register
typedef unsigned char BYTE; typedef unsigned short WORD; typedef unsigned int DWORD; //---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- #define SMBHSTSTS 0x00 // SMBus Host Status Register Offset #define SMBHSTCNT 0x02 // SMBus Host Contorl Register Offset #define SMBHSTCMD 0x03 // SMBus Host Command Register Offset #define SMBHSTADD 0x04 // SMBus Host Address Register Offset #define SMBHSTDAT0 0x05 // SMBus Host Data0 Register Offset
#define SMBHSTCNT_START 0x40 // SMBus Host Contorl -> 0100 0000 Start #define SMBHSTCNT_BYTE 0x08 // SMBus Host Contorl -> 0000 1000 Byte Data //---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- #define DPC_ADD 0xb0 #define PWMFeq 0x01 #define PWMDuty 0x02
SMBusIoWrite
void SMBusIoWrite(BYTE byteOffset, BYTE byteData)
{
outb( byteData , (g_SMBusMapIoAddr + byteOffset) );
}
SMBusIoRead
BYTE SMBusIoRead(BYTE byteOffset)
{
DWORD dwAddrVal;
dwAddrVal = inb((g_SMBusMapIoAddr + byteOffset));
return (BYTE)(dwAddrVal & 0x0FF);
}
SMBus_WriteByte
bool SMBus_WriteByte(BYTE byteSlave, BYTE pCmd, BYTE pByte)
{
SMBusIoWrite(SMBHSTADD , byteSlave & ~1 );
SMBusIoWrite(SMBHSTCMD , pCmd );
SMBusIoWrite(SMBHSTDAT0 , pByte );
SMBusIoWrite(SMBHSTCNT , SMBHSTCNT_START | SMBHSTCNT_BYTE);
return true;
}
SetDutyCycle
void SetDutyCycle(gint nDutyValue)
{
SMBus_WriteByte( DPC_ADD, PWMDuty, (BYTE)nDutyValue );
}
SetFrequency
void SetFrequency(gint nFrequency)
{
SMBus_WriteByte( DPC_ADD, PWMFeq, (BYTE)nFrequency );
}